What is a Roll Lamination Machine and How Does It Work?
A Roll Lamination Machine plays a crucial role in various industries. It offers efficient and effective solutions for protecting documents and enhancing product durability. This machine applies a thin layer of lamination to surfaces, allowing for better resilience against wear and tear.
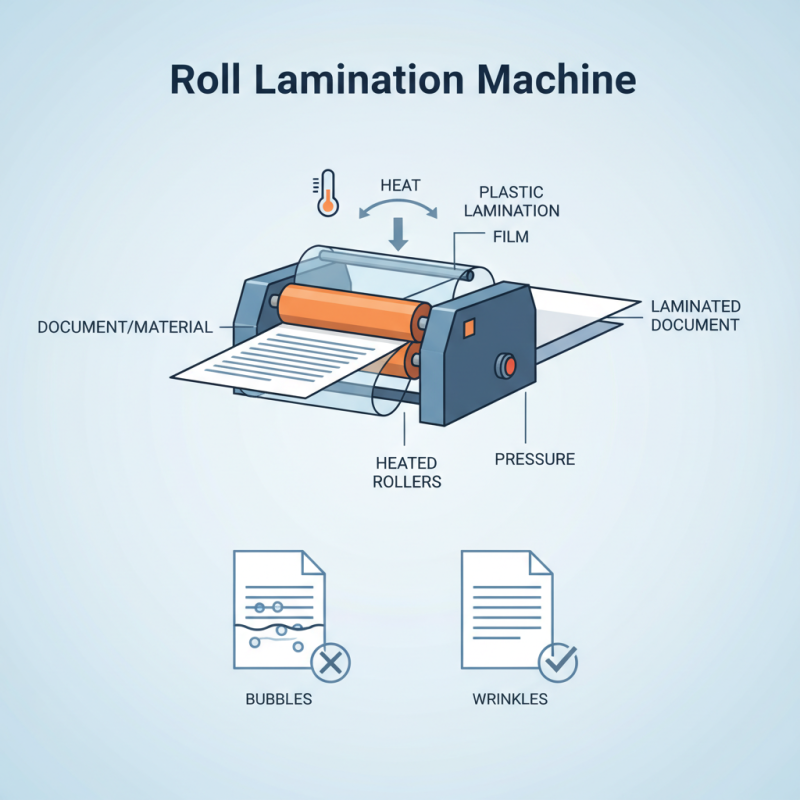
Understanding how a Roll Lamination Machine functions can demystify its applications. Users often find themselves unsure about the process. The machine heats and adheres a plastic film to the material. This creates a protective barrier, enhancing appearance and longevity.
However, the operation of a Roll Lamination Machine isn’t without challenges. Proper settings and techniques are essential for optimal results. Incorrect adjustments can lead to bubbles and wrinkles. These common pitfalls require careful attention. A well-used machine leads to efficiency, but a poorly managed one can waste materials and time.
Definition and Purpose of a Roll Lamination Machine
A roll lamination machine is an essential tool in many industries. It is used to apply a protective layer to various substrates, enhancing durability and aesthetics. This machine works by rolling two or more materials together under pressure. The process produces a laminated product that is both sturdy and functional.
The primary purpose of a roll lamination machine is to create a bond between materials. This bond can provide weather resistance, improved appearance, or added strength. Many businesses benefit from this, especially in packaging and construction. When done correctly, the results can be impressive. Yet, mistakes can happen. Improper settings may lead to bubbles or creases, affecting the final product's quality.
The machine operates through heat and pressure, which can be tricky. Temperature regulation is crucial. Too high, and you risk damaging the materials; too low might not bond effectively. Each project can present unique challenges. Adjustments may be necessary. Testing and refining the process can be time-consuming. However, these steps are critical for achieving the best results.
Key Components of a Roll Lamination Machine
A roll lamination machine is an essential tool in various manufacturing processes, especially in packaging and printing industries. Understanding its key components can help improve operational efficiency. The machine typically comprises several important elements: rollers, film supply, lamination heat source, and control interface.
Rollers are pivotal in this system. They apply pressure and heat to bond layers together. Standard roller materials include steel or aluminum, chosen for their durability. Moreover, maintaining roller alignment is crucial for achieving uniform lamination. The film supply feeds the material into the machine. Choosing the right film type is essential; it can significantly impact the final product’s quality.
Tips: Regularly inspect rollers for wear and tear. This prevents uneven lamination layers. A poorly maintained roller can cause production delays.
The heat source is another critical component. It ensures proper adhesion between layers. Some models utilize electric heaters, while others may rely on thermal oil. Each system has its pros and cons. The control interface allows operators to adjust settings easily. An intuitive interface can reduce errors and speed up training processes.
Tips: Invest time in training staff on the control interface. Proper training enhances efficiency and minimizes costly mistakes. Overall, operators should reflect on the machine’s performance regularly to identify areas for improvement. This proactive approach can boost productivity.
How Roll Lamination Machines Operate
Roll lamination machines play a crucial role in various industries, providing a method to protect and enhance printed materials. These machines use heat and pressure to apply a layer of plastic, creating a durable and often waterproof finish. According to a recent report by Smithers Pira, the global laminating market is expected to reach $48 billion by 2025. This growth highlights the significance of roll lamination in improving product longevity.
The operation of roll lamination machines involves feeding materials through rollers. The rolls heat the lamination film to its melting point, allowing it to bond with the substrate. Precise temperature control is vital. Too hot, and the material may warp; too cold, and adhesion fails. Moreover, alignment is critical. Misalignment can lead to waste and subpar quality. Approximately 20% of the production time can be lost due to misaligned sheets, based on industry studies.
Roll lamination is not just technical. It requires human oversight for quality control. Operators must keep an eye on various parameters throughout the process. They often face challenges such as film inconsistencies and machine jams. Continuous training and troubleshooting are essential. An effective roll lamination setup requires more than just machinery; it demands careful planning and adept human intervention.
Applications of Roll Lamination Machines in Various Industries
Roll lamination machines are essential in various industries. They apply a thin layer of material to surfaces. This technique offers durability and aesthetic appeal. For instance, in the automotive industry, laminated surfaces resist scratches and enhance visual attractiveness. A report from the International Laminating Association highlights that 78% of manufacturers prioritize surface enhancement in their designs.
Another significant application is in packaging. Roll lamination machines create moisture-resistant and durable packages. The food industry benefits greatly from this. A report by Packaging Strategies notes that 65% of consumers prefer products with improved packaging quality. However, some challenges arise, such as the waste generation during the lamination process.
Electronics also utilize roll lamination extensively. Devices with laminations tend to have better longevity and performance. Data from the Electronics Manufacturing Association indicates that 70% of electronic products in 2023 are designed with laminating technology to improve reliability. As industries adopt more sustainable practices, addressing energy consumption in roll lamination remains a critical area for improvement.
Advantages of Using Roll Lamination Machines over Other Methods
Roll lamination machines offer distinct advantages over traditional lamination methods. They utilize a continuous process that can significantly increase production efficiency. This machine applies heat and pressure simultaneously, creating a strong bond between layers. The uniform application ensures consistency in the finished product.
Another notable benefit is the cost-effectiveness of roll lamination. Bulk materials can be processed, reducing waste substantially. This method requires less manual intervention, making it safer for operators. However, not all materials are suitable for roll lamination, which poses limitations. Careful selection is essential to maximize advantages.
While roll lamination machines excel in speed, they may not have the flexibility needed for small runs or custom orders. Adjustments can take time. This could lead to delays in production. Manufacturers should weigh these factors carefully when opting for this technology. Balancing efficiency with adaptability is key for optimal results.
